Automated Welding System MIG vs. TIG: Which Fits Your Application?
Automating your welding process boosts throughput, weld quality, and safety. However, choosing a welding robot for manufacturing that best fits your application is crucial to gaining these efficiencies. This blog explains the fundamentals of robotic MIG and TIG welding, the difference between MIG and TIG in automation, and guidance on choosing the right robotic welder for your operation.
MIG and TIG welding are the two most common types of welding used in the manufacturing industry and both can be automated. The benefits of robotic welders include:
- Increased productivity: Robotic welders produce higher-quality welds faster than manual welders, maximizing productivity.
- Improved quality: Robotic welders are more accurate and precise than manual welders, enhancing quality of the weld and finished products.
- Reduced material waste: Because robotic welders are programmed with precise specifications, less filler material is used and wasted, and errors are reduced, which can add up to big savings.
- Enhanced safety: Welding is a dangerous, tiring, and repetitive process. Automating welding minimizes hazards and fatigue, improving facility safety and freeing manual workers for other tasks.
In some applications, manufacturers also explore collaborative robotic welding (cobot welding) solutions, which allow human workers and robots to safely share workspace while improving weld consistency and throughput.
Robotic MIG Welding
MIG welding is a type of gas metal arc welding (GMAW) that continuously feeds a consumable wire electrode into the weld as it is being made. The wire serves as the filler material that fuses two metal objects together.
Robotic MIG welding produces high-quality welds quickly and continuously because the filler material does not have to be heated all the way through to create the weld. This makes MIG welding the preferred technique for welding thick metals or large pieces of metal, such as sheet metal. The use of a filler material also means robotic MIG welding can be used to weld dissimilar metals or metals with very high melting points, such as aluminum and stainless steel.
Automating MIG welding maximizes productivity and throughput, especially when working with large workpieces. MIG welding is also commonly used in cobot welding setups where operators work directly alongside a collaborative robot to manage part positioning or finishing tasks.
Robotic TIG Welding
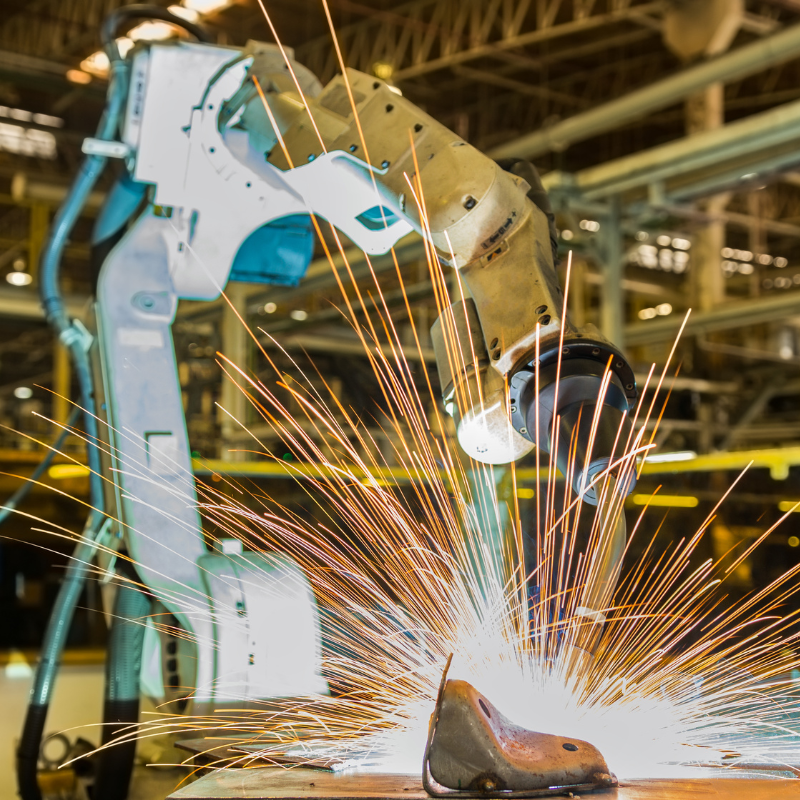

TIG welding is a type of gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) in which currents run through the metal to fuse two parts together. The TIG process relies on a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create a weld arc that heats and melts two metal materials to join them together.
Robotic TIG welding is a slower, but more precise process than MIG welding, so it is suitable for welding thin metals and small, intricate workpieces. TIG welding can weld electrically resistant metals and more metal materials than MIG welding.
Automating TIG welding will increase efficiency of the process, but the real goal of robotic TIG welding is to ensure high-quality, precise welds. For applications that require operator involvement or part manipulation, collaborative robotic welding systems can support TIG processes by improving repeatability while maintaining hands-on control.
Automated Welding Systems: MIG vs. TIG
While both robotic MIG and TIG welding systems will increase safety, productivity, and quality, and both are arc welding methods that use an inert gas to prevent corrosion of welding electrodes, there are significant differences.
The following chart compares automated MIG and TIG welding.
| Characteristic | Robotic MIG welding | Robotic TIG welding |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Faster process than TIG welding, especially when welding large workpieces or making thicker welds. | A slower process than MIG welding, but more efficient than manual welding. |
| Precision | Produces a high-quality weld, but is not as precise as TIG welding. | Produces a very precise weld, making it suitable for thin metals or detail work where clean and precise welds are required. |
| Versatility | Quickly makes large or thick welds and can weld two different metal materials together. Good for metals with high melting points. | Can precisely weld small intricate parts, thin materials and many different metals, including those that are electrically resistant. Can weld more metal types than MIG welding. |
| Weld automation robot applications | Quickly welding large workpieces or making thick welds, welding operations where precision or appearance aren’t critical. Often used in automotive manufacturing for chassis and large parts, heavy-duty machinery and sheet metal welding. | Making neat, attractive and precise welds, especially with thin metals or intricate workpieces, processes where accurate welds are critical. Often used in aerospace component manufacturing, manufacturing of precision equipment and electronics manufacturing. |
Choosing a Welding Robot for Manufacturing
Choosing the right automated welding solution is critical to improving weld quality and boosting throughput, but selecting the wrong type of robotic welder will offset the benefits of automation. Depending on operator workflow and production volume, you may also consider cobot welding systems. These collaborative robotic welding solutions offer a flexible and cost-effective entry point into automation for smaller batch sizes or mixed-part manufacturing.
Important factors to consider when choosing a welding robot for manufacturing include:
Welding materials: Does your operation weld large or thick pieces of metal (MIG welding) or small intricate parts or thin materials (TIG welding)? Also consider the material you are welding. Are they dissimilar metals or do they have a high melting point (MIG welding) or do you weld a wide variety of metals (TIG welding)? Ensure that the robotic welding system you choose is suitable for the metal material and welding specifications.
Weld quality requirement: Does your application demand a clean and precise weld, such as electronics manufacturing or aerospace components (TIG welding) or do you weld large pieces of metal where a less accurate weld is acceptable, such as sheet metal welding (MIG welding)?
Goal of automating the welding process: Are you looking to increase the throughput of your welding operation (MIG welding) or is a more precise weld the goal (TIG welding)?
Let HTE Help You Choose between Robotic TIG Welding and Robotic MIG Welding
Selecting the right robotic welder for your application is essential to optimizing welding throughput and quality. Contact the experts at HTE to ensure that you choose the best automated welding method for your operation so you can start welding smarter and more efficiently today.



