Why You Should Choose a Rotary Screw Compressor for Manufacturing
Choosing the right air system for your business is key to achieving high levels of energy efficiency and performance. Most manufacturing operations require a constant flow of compressed air, making rotary screw air compressors, which run reliably under continuous operation, the ideal technology for heavy-duty industrial applications.
This blog explains how rotary screw compressors work and why they’re suitable for operations that need a reliable, continuous-duty air compressor. Selection guidance will also be provided.
What is a Rotary Screw Air Compressor?
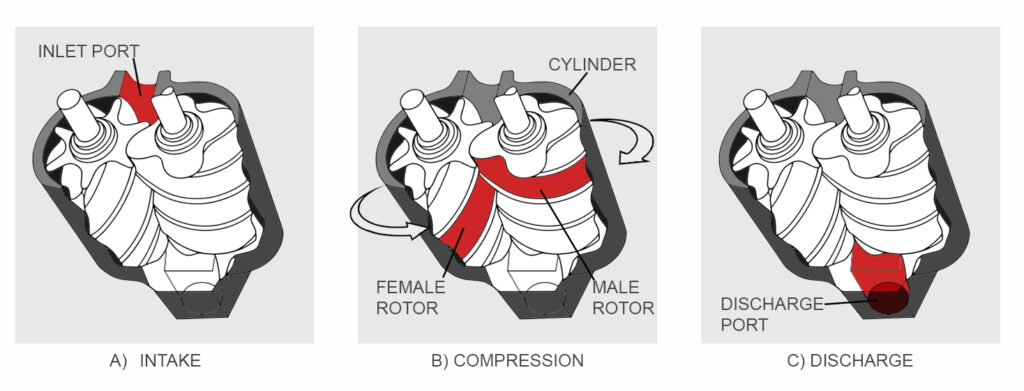
Rotary screw machines compress air using two intermeshing helical rotors that spin continuously. Sometimes called twin screw compressors, they are designed to run reliably under continuous duty operation.
How Rotary Screw Compressors Work
Air is drawn into the compression chamber and trapped between the rotors. As the rotors turn, the air is compressed, pushed out of the chamber, and moved through the system, where it is cooled, dried, and ready for use.
As the rotors continue to turn, air is continuously compressed, producing a constant stream of pressurized air without a rest period. This continuous supply of compressed air, called a 100% duty cycle, provides 24/7 operation.
Rotary Screw vs. Reciprocating Compressors
When tasked with buying an industrial air compressor, you may consider reciprocating and rotary screw air compressors. While both are solid technologies, they differ in design, operation, and application. A comparison will help you make an informed decision.
What is a Reciprocating Compressor?
In a reciprocating compressor, pistons, driven by a crankshaft, move back and forth in a cylinder to compress air.
Reciprocating compressors provide intermittent air flow because they require a rest period to prevent overheating and premature wear. This means reciprocating compressors offer lower duty cycles (for example 50% or 60%) than rotary screw compressors, which are designed for 100% duty cycles.
An intermittent duty cycle is suitable for operations that don’t need continuous airflow, such as small automotive shops and construction sites. When used in continuous duty applications, reciprocating compressors may experience failure.
This head-to-head comparison of key features will help you decide which compressor type best fits your application.
| Performance Metric | Rotary Screw Air Compressor | Reciprocating Compressor |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Reliably run at a 100% duty cycle for continuous, 24/7 operation. Screw compressors lose energy efficiency when operated intermittently. | Provide intermittent airflow and lower duty cycles. Reciprocating compressors fail prematurely when operated continuously. |
| Typical Applications | Used in industrial applications that require large volumes of air in a steady, continuous flow. General manufacturing, food and beverage, automotive, and pharmaceutical industries are typical applications. | Used in applications that require short, intermittent bursts of air. Small autobody shops, construction sites and small businesses are typical applications. |
| Efficiency | The air compression process results in low energy loss, making screw compressors efficient. Variable speed drive (VSD) motors further boost efficiency. | The motion of the pistons causes fluctuations in air flow, making reciprocating compressors less energy efficient. |
| Maintenance Requirements | Fewer moving parts mean less wear and tear and fewer potential failure points. | More components increase maintenance requirements and potential failure points. |
How to Choose a Rotary Screw Compressor for Manufacturing
While the best technology is the one that meets the requirements of your operation, many heavy-duty applications need an air compressor for continuous use, so industrial users choose a rotary screw air compressor for manufacturing due to their efficient and reliable continuous-duty operation.
To choose a rotary screw compressor for manufacturing operations, consider the size and features you’ll need.

Compressor size:
Proper sizing ensures efficiency and minimizes wear and tear. To get the right size compressor, you must determine your air flow (cubic feet per minute, CFM) and pressure (pounds per square inch, PSI) requirements.
To find the CFM requirement for your rotary screw air compressor:
- Find the CFM requirement for each tool. Every pneumatic tool has a specific CFM rating provided by the manufacturer. Check the tool itself, the product manual or the manufacturer’s website for this information.
- Add the CFM of all the tools used simultaneously. To calculate your CFM requirement, add up the CFM requirements for each of the tools that will be operating at the same time.
- Multiply that number by 1.5 to provide a buffer. To account for pressure drops and peak demand, multiply the CFM number from above by 1.5.
- This number is your CFM requirement.
To find the PSI requirement for your rotary screw air compressor:
- Find the tool with the highest PSI rating. There is no need to add the PSI of all the tools.
Choose a rotary screw air compressor that provides the required CFM at the necessary PSI rating
Oil-lubricated or Oil-free
Your application determines whether you need an oil-lubricated or oil-free compressor. For example, a food manufacturer that requires contaminant-free air must get an oil-free unit, while a plant that powers pneumatic tools with compressed air can use an oil-lubricated machine.
Fixed speed or VSD
Fixed-speed rotary screw compressors efficiently supply continuous streams of air. But variable speed drives (VSD) adjust the compressor’s output to match the demand, which increases energy efficiency in continuous applications and those with fluctuating demand.
Find the Right Rotary Screw Air Compressor for Your Business

Looking to upgrade to a more efficient and reliable compressor for your continuous-duty application? The air compression experts at HTE are standing by to help you select and size a rotary screw air compressor for your application.